Enlargement of the prostate gland
What is BPH?
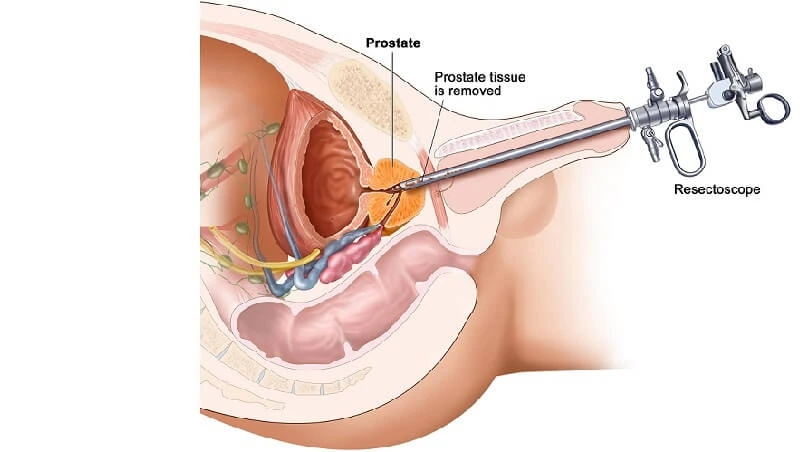
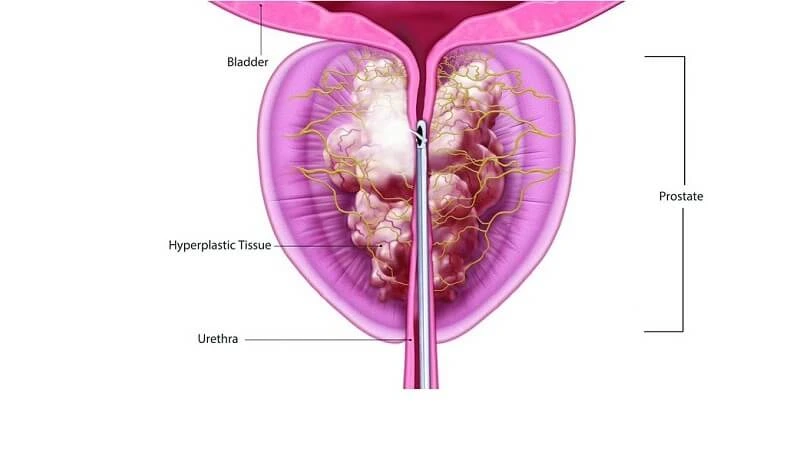
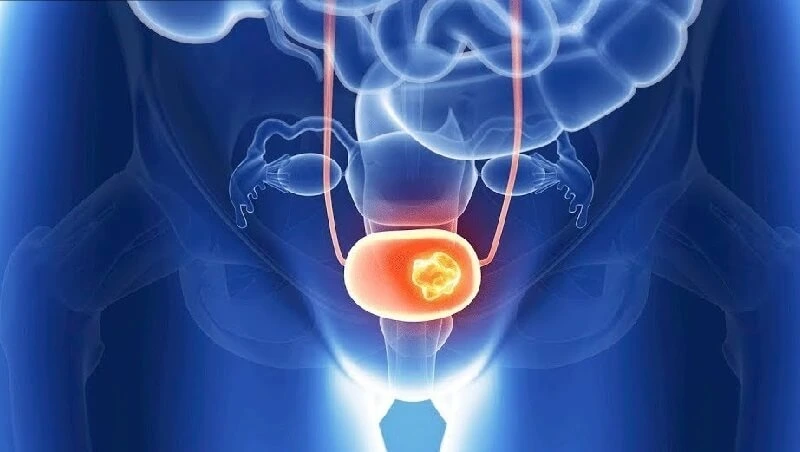
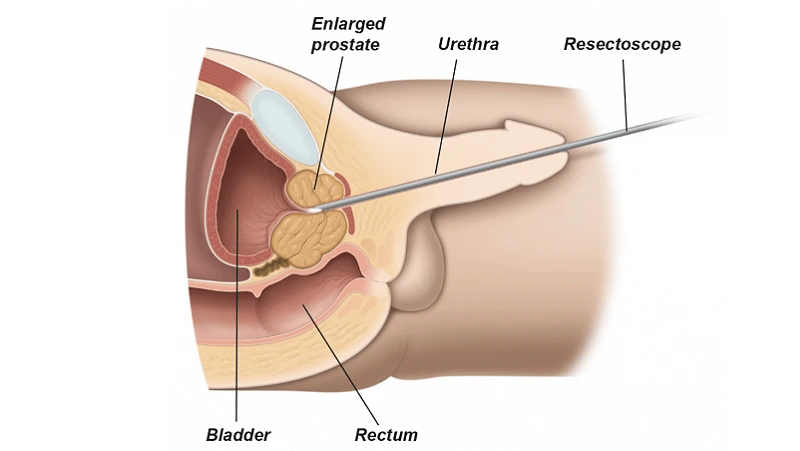
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, commonly seen in men as they age. The prostate surrounds the urethra (the tube that carries urine from the bladder), so when it enlarges, it can squeeze or block the flow of urine.
Who Gets BPH?
- Mostly affects men over 50
- By age 60, more than 50% of men may have symptoms
- Risk increases with age, family history, obesity, and lack of physical activity
Common Symptoms
- Frequent urination (especially at night)
- Urgency to urinate
- Weak urine stream
- Difficulty starting urination
- Dribbling at the end of urination
- Incomplete emptying of the bladder
- Urinary retention (in severe cases)
How is BPH Diagnosed?
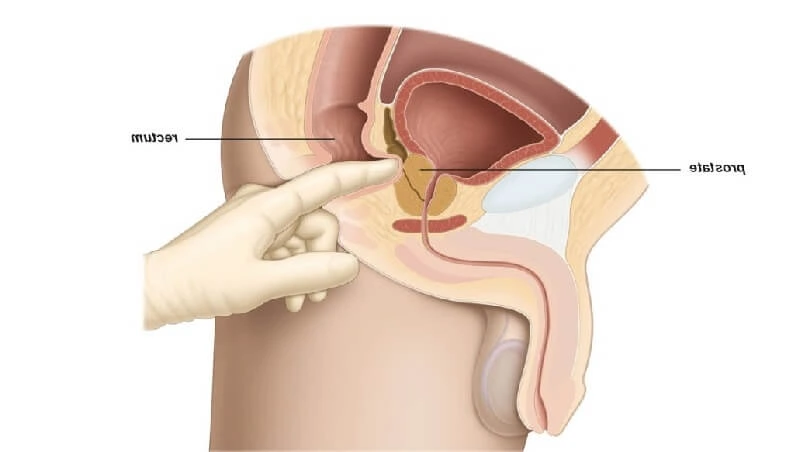
- Physical examination (including digital rectal exam)
- Urine tests (to rule out infections)
- PSA blood test (to check prostate-specific antigen)
- Ultrasound (to assess prostate size and bladder function)
- Uroflowmetry (measures urine flow speed)
- Cystoscopy (in some cases)